Find results that contain all of your keywords. Content filter is on.
Search will return best illustrations, stock vectors and clipart.
Choose orientation:
Make it so!
You have chosen to exclude "" from your results.
Choose orientation:
Explore cartoons & images using related keywords:
thymine
h1
h4
h3
endoplasmic
nucleotide
telomere
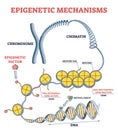
h2a h2b tail histone proteins base pair presentation peptide polypeptide amino laboratory polymerase icon genetic code deoxyribonucleic acid antiparallel information dna packaging macromolecule concept chemistry eukaryotic genes molecule guanine cytosine chromatid chromatids centromere adenine education sequence microscopic diagram chromosomes biological biochemistry chromatin nucleusHistone Protein Vector Illustration
Designed by
Title
Histone protein #321336756
Description