Find results that contain all of your keywords. Content filter is on.
Search will return stock photos and royalty free images.
Choose orientation:
Make it so!
You have chosen to exclude "" from your results.
Choose orientation:
Explore cartoons & images using related keywords:
anatomy
biology
bloodvessels
body
cardiac
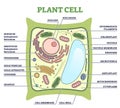
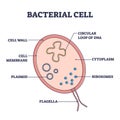
cell
connectivetissue
contraction endomysium epimysium fascicle fiber healthy human illustration medical medicine muscle musclecell musclefiber muscular perimysium science skeletal smooth striated tendons tissue vesselsInner Parts Of Muscle Tissue Stock Image
Designed by
Title
Inner Parts of Muscle Tissue #43014589
Description